Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Securing Access To Resources
A Google survey found that at least 65% of people reuse passwords across multiple services, leaving them vulnerable to hackers gaining access to their sensitive accounts. One way to protect the accounts against such vulnerability is to introduce an additional verification step during login – multi-factor authentication (MFA).
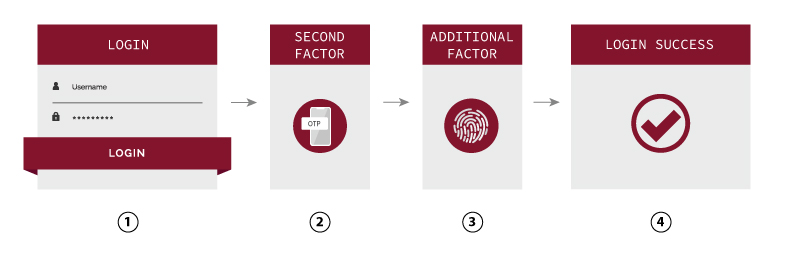
MFA – the need of two or more methods of authentication factors to verify user’s identity to grant access to applications or online accounts. It provides an additional layer of defense to your account, making it less likely to be compromised. Different factors of authentication include:
Something you know – e.g. password, PINs
Something you have – e.g. smartphone, OTP token
Something you are – e.g. fingerprint, biometrics
How MFA works?
Stepping Up with Adaptive Authentication



Adaptive or Risk-Based Authentication
Adaptive authentication, also known as risk-based authentication, challenge if additional factors are required by analyzing context and behaviour to determine the risk associated with each login attempt. Additional factor may be skipped when trust is high. Context and behaviour being considered may include:
- Location – Where is the user logging in from?
Device – Is the user using the same device as prior?
Network – Is the user logging in from the same IP as prior?
These considerations help determine whether additional authentication factor is required. Likewise, access to sensitive data may be prompt with additional factors during login.
Key Benefits of i-Sprint MFA Solution
- Flexibility to deploy various authentication methods from different vendors
- Security services APIs for application integration and shield the complexity of token integration
- End-to-end encryption during authentication session; protection of data in transit
Interested in Learning More?
Connect with a specialist to address your queries and find solutions tailored to your needs.
